
National Achievement And COVID Education Inequities Demand A New Model Of Schooling
The Latest Obstacles to Reopening Schools Forbes | October 29, 2020
By Jeanne Allen, Founder and CEO of CER It’s more than alarming to read, and even more shocking to consider, that the nation’s high school seniors cannot perform math or reading at their grade level. That’s this week’s headline out of the National Assessment of Education Progress and the National Center for Education Statistics, a non-political government agency that has for more than 4 decades assessed the achievement of students every couple of years in most major subjects in 4th, 8th and 12th grade.
What’s particularly jolting about this news is that, as special interests and policymakers bicker about how and whether to even open schools or improve their virtual capacity to teach, we can only imagine the relative achievement of our students coming out of a major lack of education during these many months, for most students.
As widely reported, health officials are arguing that it’s more likely our students will suffer from devastating social and academic declines than health threats if they don’t get back to where they are being educated. Whether that means a traditional school setup or some version of it is not debated. But let’s take a look at the 90% of the schools participating in the semi-annual sampling of student proficiency and whether even demanding schools reopen the same way is worth it.
Most students attend a school that is made of “bricks and mortar,” as the saying goes, assigned there by their zip code, a policy that has become inherently inequitable – and racist. According to 50 CAN’s Derrell Bradford, reporting on the FDR 1930s era home loan effort to boost the economy, “the federal government made color coded maps of every metropolitan area of the country, and described some places as desirable, some less desirable and some as hazardous. And if you lived in one of these areas, you couldn’t get one of the home loans that everyone else got. It drove down property values. Even though redlining has been outlawed, the school zones align with the map from the 1930s.”
Today, money is less the issue in these neighborhoods. First, they are heavily subsidized by federal and state governments, and have disproportionate ratios of administrators to students, in other words larger bureaucracies that impede fast turn around solutions. Second, they are assigned the least qualified educators by districts that rank them according to seniority and experience (not demonstrated performance). Newer, less experienced teachers end up in the less desirable school assignments, with less pay and fewer resources. Their parents are less likely to have graduated from High School or college, and less likely to be able to get their child out of a bad school because there are few options that are better for free. That’s why you’ll most often see inner city or rural schools failing to deliver results, and why typically scores on assessments like the National Assessment of Educational Progress are lower among poor and minority students.
But even the achievement of higher performing, more affluent students in this nation could be considered failing by most measures. Only 37 percent of 12th graders are at above proficient in reading. The report card found that “in 2019 twenty-six percent of all twelfth-graders in the nation reported that they never read stories or novels, and fifty-one percent of twelfth-graders reported that they never read poems outside of school. Larger percentages of lower-performing students (below the 25th percentile) than higher-performing students (at or above the 75th percentile) reported never reading these types of literary texts.”
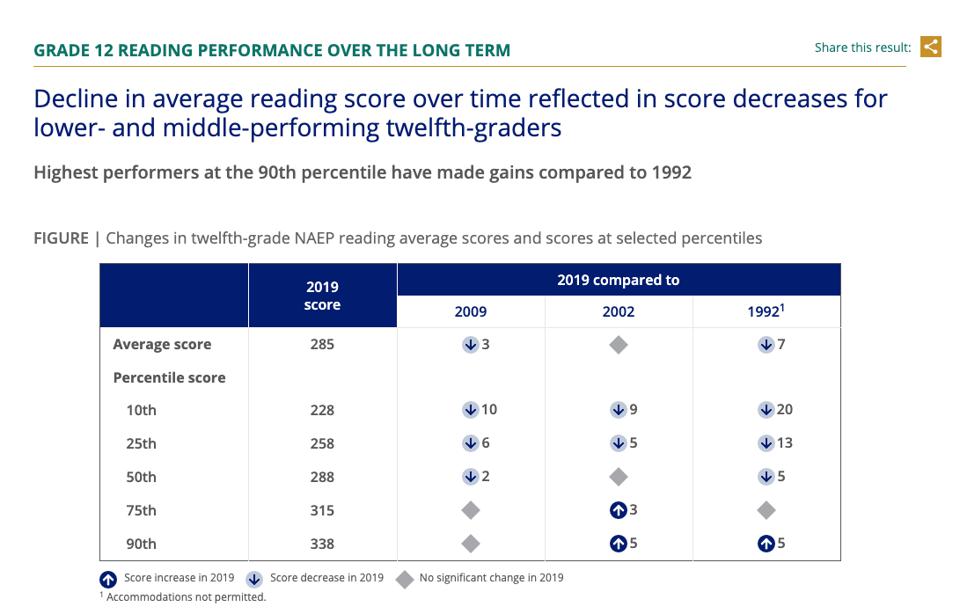
Grade 12 Reading Performance Over the Long Term Shows A Decline In Average Reading Scores NAEP | NATION’S REPORT CARDSo while education is vital, opening up schools in systems that cannot be counted on to ensure students accomplish reading proficiency sans a pandemic is not the answer. Not only is failure for too many students the norm, but the evidence is clear – districts are not equipped by temperament or structure to respond to the urgency of a crisis.
In April 2020, Fairfax County, Virginia, often called one of the best districts in the country, started and then overnight suspended its remote education program for its nearly 200,000 students because administrators could not correctly launch its online program, Blackboard. Flash forward four months, to September 22, when the Fairfax County School Board voted to bring back only 6,000 students, scheduling another 4,000 with special needs shortly after, despite a low COVID transmission rate. Meanwhile, the local teachers union remains opposed to any kind of return to in person instruction, and is staging “sick outs.” The superintendent told the Washington Post. “Honestly, I feel sometimes like I’m in the middle of a Goldilocks fairy tale, we don’t want to go too hot. We don’t want to go too cold. We want to do it just right: And just right is a measured approach starting with small cohorts of kids.”
Just right? For whom?
A similar scenario is unfolding in other Virginia counties, such as Prince William and Loudoun Counties, where a hodge-podge of alternating days with the youngest kids coming to school and older kids staying home has parents fuming.
Reported one parent on Twitter, “distance learning in Loudoun is a mess. Kids who were straight A students are getting Cs online, crushing their college chances. My kid hasn’t walked into a school since March.”
At the opposite end of the country, California’s rationale for leaving students out of school is being called into question. Poor students are suffering, and were the least likely to receive resources during the earliest days of the pandemic. According to Politico, state legislators are getting more than impatient with the Governor. They “demanded on Tuesday [that the governor issue] more specific statewide guidelines for school reopening, emphasizing that equity gaps will otherwise grow as some students return to classrooms faster than others.”
“The unequal pace of school reopenings is exacerbating California’s educational inequity,” screamed a recent Los Angeles Times headline. Yet school reopenings are plagued by fear, not data. “No one has created a consistent definition for the intimidating word ‘outbreak,’ so it has often come to mean ‘more than one case.’ We have little idea at this point how many of those infected people brought the virus into their schools from outside and how many were infected at school,” opined the Times. “It’s hard to see the scientific reasoning behind some of the county’s plans.”
The number of observers, press, researchers leaders saying precisely that everywhere, is growing. “There is very little evidence that Covid spreads in schools,” said America’s most popular -and cautious- Governor this week, Massachusetts’ Charlie Baker. He has expressed his frustrationwith schools staying closed, calling out districts to reopen schools with the structure and guidance his administration put out with health authorities in July, especially given evidence of in-person learning success elsewhere.
“We have one of the best active demonstrations about in-person learning going on anywhere right now which is the parochial schools. They are located for the most part almost completely in

SALEM, MA: October 21, 2020: Massachusetts Governor Charlie Baker joins Salem Mayor Kim Driscoll to discuss the planned closures in the Salem area for Halloween and the days leading up to it due to COVID-19, at the Mayor Jean Levesque Community Life Center in Salem, Massachusetts. (Staff photo by Nicolaus Czarnecki/MediaNews Group/Boston Herald) MEDIANEWS GROUP VIA GETTY IMAGEShigh risk communities,” primarily serving people of color. “They have almost 30,000 kids, 4,000 teachers and staff; fully in person since August in places like Lynn, Revere, Brockton, Boston.” There are fewer than 40 cases of Covid across all those schools, says the Governor, “and they came from outside in.”
Unfortunately, the evidence isn’t enough to get most districts moving. State by state, city by city, district officials keep announcing delays and union officials oppose reopenings. According to the Center on Reinventing Education, “even the best districts are struggling to implement plans and provide consistent, quality learning.” The University of Washington-based research organization has been studying the behavior of school organizations and districts since spring, and reports wildly uneven, inequitable responses, from all levels, sometimes despite the best efforts.

Districts have the opportunity to rebuild and reimagine themselves to address root inequities that have long plagued education. THE EVIDENCE PROJECTThe Solution
We must create the opportunity for willing parents to hire the schools and teachers that best work for their kids. They can be public – like charters – private, pods or microschools, or even individualized tutoring, but they would work for the family, by their choosing.
Billions are subsidizing near empty school buildings, contracts, empty buses and so much more. Just like many of us have had to cancel our leases on real estate that is unused during fiscal difficulties, districts should give up costly and underutilized buildings and be forced to give willing education organizations, educators and parents access to those or any of the resources for which their taxes have paid dearly.
Maybe schools that want to be open would expand. Maybe microschools or blended learning environments or apprenticeship programs would emerge. Perhaps hundreds of parents would choose to pool their resources and hire teachers and tutors. Whatever the outcome, it has to be better than sustaining a system that fails to put student interests ahead of rules and contracts.
Asks 50 CAN’s Bradford, how do we address decades of inequity and injustice? “Stop assigning kids to public schools based on their home address and improve the way we fund public education, because no one size fits all solution is going to fit all children.”Follow Jeanne on Twitter or LinkedIn or some of her other work here.
Founded in 1993, the Center for Education Reform aims to expand educational opportunities that lead to improved economic outcomes for all Americans — particularly our youth — ensuring that conditions are ripe for innovation, freedom and flexibility throughout U.S. education.

